
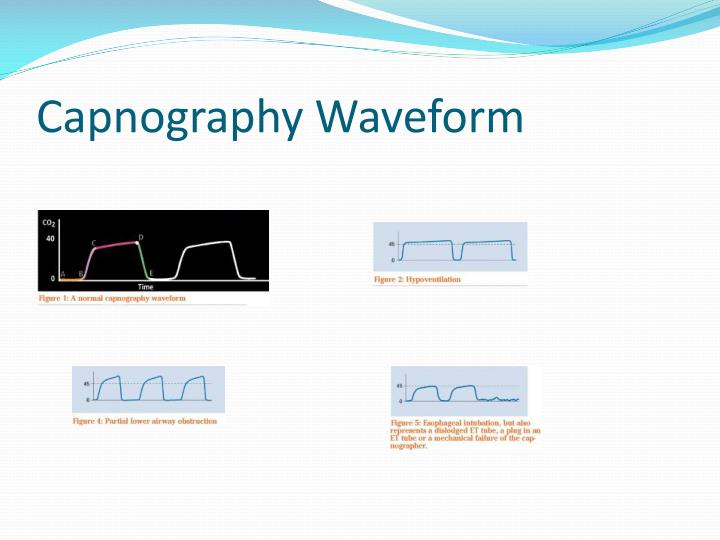
confirming tracheal rather than esophageal intubation.monitoring the adequacy of pulmonary blood flow.monitoring the integrity of the ventilator circuit and artificial airway.evaluation of the severity of pulmonary disease.evaluation of maximum exhaled CO 2 concentration as a reflection of the PaCO 2.Evaluation of the capnogram may be useful in the measurement of adequacy of alveolar ventilation, airway integrity, cardiopulmonary function, and ventilator function. The capnogram provides a measurement of the end-tidal partial pressure of CO 2 (P et CO 2), which is frequently a reliable estimate of the arterial partial pressure of CO 2. When inspiration occurs, the CO 2 concentration declines rapidly as CO 2-free gas enters the airway, producing a rapid sharp downstroke. This change in CO 2 concentration produces the alveolar plateau. As alveolar gas begins to dominate the exhaled gas volume, the change in CO 2 concentration decreases significantly. As exhalation continues, CO 2 concentration begins to rise as gas from the alveoli starts to empty, creating a rapid sharp uprise. The Normal CapnogramĪs the patient begins to exhale, the initial sample contains CO 2-free gas from the tracheal dead space that has not been involved in gas exchange this creates a zero baseline. Sidestream capnograms withdraw gas from the patient’s airway. Mainstream capnograms use a sample measurement chamber that is placed in-line with the patient’s airway. The waveform produced is called a capnogram.Īnalysis of CO 2 concentration is performed by infrared absorption spectrophotometry utilizing mainstream or sidestream sampling. Pulse oximetry and capnography are two tools available for assessing ventilation and perfusion status, especially in the prehospital and emergency department arenas.Ĭapnography is the graphic display of airway CO 2 concentration or partial pressure measurement as a function of time. With more sophisticated and cost-appropriate monitoring equipment and the requirement for maintaining greater patient safety, another “vital” has been added to patient assessment: ventilation and perfusion status.

They generally include blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate, temperature, neurologic status, and color. Vital signs comprise the cornerstone of patient assessment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
